Difference between revisions of "PAL (Chip)"
Omega Haxors (talk | contribs) m |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a programmable logic device | + | A [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Programmable_Array_Logic Programmable Array Logic (PAL)] is a programmable logic device used to implement any logic function in only one digital circuit. This is useful in applications where you need to reuse the same component for various tasks, and don't want to constantly replace your components. PALs are programmed via a Karnaugh map. They may seem complicated at first, but it's very intuitive once you understand the underlying mechanics. |
| − | any logic function in only one digital circuit. | ||
| − | |||
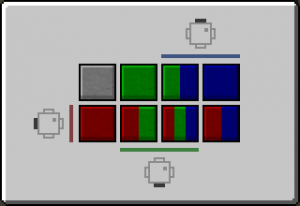
| − | PAL | + | First the PAL takes the Red Blue and Green inputs and uses it to point at a certain square in the map. Whatever the value inside that square is, will be the output of the PAL. The first square is pointed to if no buttons are pressed at all. Any square in the path of a colored line will be given that color, which then determines which inputs it requires to be pointed at. |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:PAL Color Map.png|thumb]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Digital chips]] | [[Category:Digital chips]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:44, 31 August 2018
A Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a programmable logic device used to implement any logic function in only one digital circuit. This is useful in applications where you need to reuse the same component for various tasks, and don't want to constantly replace your components. PALs are programmed via a Karnaugh map. They may seem complicated at first, but it's very intuitive once you understand the underlying mechanics.
First the PAL takes the Red Blue and Green inputs and uses it to point at a certain square in the map. Whatever the value inside that square is, will be the output of the PAL. The first square is pointed to if no buttons are pressed at all. Any square in the path of a colored line will be given that color, which then determines which inputs it requires to be pointed at.